
Role of MSMEs in Achieving Net Zero and Carbon Credits
By adopting sustainable practices and earning carbon credits, MSMEs can become powerful drivers in the global Net Zero mission, says Darshana Thakkar. With targeted strategies across sectors like energy, manufacturing, and transportation, MSMEs not only reduce their carbon footprint but also unlock new growth opportunities and financial benefits, contributing to a resilient, sustainable future.
![[object Object]](https://admin.industrialautomationindia.in/storage/articles/article-nBXmxOdki3xPglK8LjsogA1AKELQqvwIxPruxOTH.jpg)
By adopting sustainable practices and earning carbon credits, MSMEs can play a vital role in the global Net Zero mission, says Darshana Thakkar.
As the world faces the escalating impacts of climate change, the concept of Net Zero has become a critical goal for governments, industries, and societies alike. Net Zero refers to balancing the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere with the amount removed, achieving a neutral impact.
Greenhouse gases are responsible for large no of natural calamities and increasing risk to human survival on the Earth. In addition to releasing planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions, burning fossil fuels also generates localised air pollutants — such as soot (delicate particulate matter, or PM2.5) and smog (ozone) — that increase the risk of death from stroke, heart disease, lung cancer, and respiratory illness among those exposed.
The Paris Agreement of 2015 set the stage for this mission, urging countries to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Today, more than 140 countries, representing 90% of global GDP, have committed to Net Zero targets. However, achieving this ambitious goal requires collective action across sectors, technological innovations, and policy reforms.
The global efforts
- 2015 – 196 countries adopted the historic Paris Agreement to reduce global warming and build resilience to climate change, aiming to limit warming to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- 2015-2017 – Stakeholders of the agreement began submitting climate action plans known as nationally determined contributions (NDCs). Even if fully implemented, initial commitments would only be enough to slow warming to 3 degrees.
- 2020-2021 – In the lead-up to the COP26 climate talks, countries have begun revising their NDCs to strengthen climate action. With science affirming a shrinking window of opportunity, the plans must include urgent efforts to cut carbon emissions and reach net zero by 2050.
- 2030 – To keep warming to 1.5 degrees, all the countries must cut emissions by at least 45 percent compared to 2010.
- 2050 – The transition to net zero emissions must be fully complete.
Climate crisis calls for rapid transformation of societies
Despite all the Paris Agreement and pledges by many countries to contribute to net zero and efforts, the stakeholders, including the governments of all nations and industries, are far behind the targets set under the Paris Goal. There is no credible pathway to 1.5 degrees by 2030 so far. It is calling for urgent systematic transformation to prevent climate disasters.
The Emissions Gap Report 2022 finds that the world must cut emissions by 45 percent to avoid global catastrophe.
Let us explore here the various sectors worldwide that are contributing to the Net Zero mission through decarbonisation strategies, green technologies, and sustainable practices. The MSMEs in the following sector can adopt certain strategies to support the net zero mission.
1. Energy Sector: Transitioning to Renewables and Clean Energy
The energy sector is the largest contributor to global emissions, accounting for approximately 73% of total greenhouse gas emissions. To achieve Net Zero, the sector is focusing on:
- Renewable Energy Expansion by adopting solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power to replace fossil fuels.
- Use of Green Hydrogen and Ammonia.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies in power plants and industrial processes.
- Energy Efficiency through Smart grids, IoT-based monitoring, and energy storage systems.
2. Transportation Sector: Decarbonising Mobility
The transportation sector accounts for around 25% of global CO2 emissions. The shift towards low-carbon transportation is vital for Net Zero.
- Adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Adoption of Alternative Fuels like biofuels, synthetic fuels, and hydrogen-powered vehicles.
- Promoting Public Transport and Shared Mobility
- Use of AI and route optimisation to reduce fuel consumption in freight and logistics.
3. Manufacturing and Industry: Sustainable Operations
- Energy-efficient manufacturing by Deploying automation, robotics, and AI
- Circular Economy Practices by Embracing recycling, reusing, and repurposing
- Low-carbon materials usage like green steel, low-carbon cement, and bio-based plastics.
- Investing in reforestation projects and carbon credits to offset emissions.
4. Construction and Real Estate: Sustainable Infrastructure
The construction sector contributes around 40% of global energy-related CO2 emissions.
- Green Building Standards such as LEED, BREEAM, and GRIHA-certified sustainable buildings.
- Energy-efficient materials such as low-carbon concrete, recycled steel, and sustainable insulation.
- DesigningNet Zero Buildings with solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient systems.
- Smart Infrastructure by Integrating IoT-based energy management systems.
5. Agriculture and Food Production: Sustainable Farming
Agriculture accounts for around 18% of global emissions, mainly from livestock, deforestation, and fertilizer use.
- Precision Agriculture by Leveraging AI, IoT, and drones.
- Regenerative Farming Practices like crop rotation, reduced tillage, and organic farming.
- Reducing meat consumption by promoting plant-based and lab-grown meat reduces methane emissions.
- Reducing food waste and promoting farm-to-fork models.
6. Retail and Consumer Goods: Sustainable Production and Consumption
Consumer goods production and consumption drive emissions through packaging, transportation, and waste.
- Use of biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable packaging materials.
- Ethical Sourcing Ensuring fair-trade practices and low-carbon supply chains.
- Waste Reduction by Implementing zero-waste policies and encouraging circularity.
- Carbon-neutral brand by investing in carbon offset projects.
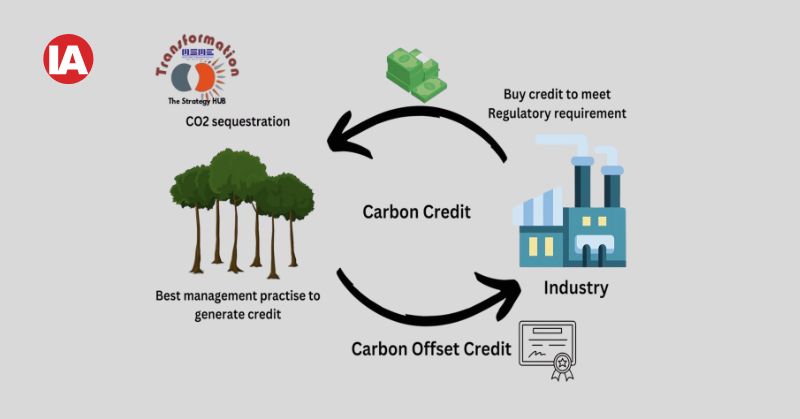
By contributing to Net Zero MSMEs can reap the benefits of carbon credits. Carbon credits are tradeable certificates representing the reduction or removal of one metric tonne of CO2 or its equivalent from the atmosphere. Businesses earn carbon credits by adopting sustainable practices that reduce their carbon footprint. These credits can be:
- Sold or traded on carbon markets to companies aiming to offset their emissions.
- Used to comply with regulatory obligations or voluntary sustainability goals.
For MSMEs, participating in carbon credit programs not only supports the Net Zero mission but also offers financial incentives and enhances their sustainability credentials.
Carbon credit benefits for MSMEs
- Generate additional revenue by selling carbon credits in global and domestic markets.
- MSMEs with carbon credit projects are more likely to access green financing.
- Improve brand reputation and marketability make MSMEs preferred partners for large corporations with ESG commitments.
- In some regions, tax rebates and credits are provided for sustainable practices.
- By proactively reducing emissions, MSMEs can stay ahead of emerging carbon regulations, avoiding future penalties.
Steps for MSMEs to avail carbon credits
Step 1: Assess the Carbon Footprint
- Conduct a Carbon Footprint Assessment (CFA) to measure emissions.
- Identify areas where emissions can be reduced through eco-friendly practices.
Step 2: Implement Carbon Reduction Projects
- Adopt energy-efficient technologies.
- Engage in afforestation, reforestation, or waste-to-energy projects.
Step 3: Register with Verified Carbon Credit Programs
MSMEs must register their projects with certified carbon credit verification bodies, such as:
- Gold Standard
- Verra (VCS)
- Global Carbon Council (GCC), and
- Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) under the UNFCCC.
Step 4: Verification and Validation
- Independent auditors verify the emission reduction achieved by the project.
- Once verified, carbon credits are issued.
Step 5: Trade or Sell the Carbon Credits
MSMEs can sell their credits on carbon trading platforms like:
- Carbon Trade Exchange (CTX).
- Climate Action Reserve (CAR).
- Indian Carbon Market (ICM).
Several MSME sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, food processing,textile, apparel, logistics, and transport sectors can leverage the benefits of carbon credit.
Government support and incentives for MSMEs
The government offers various schemes to support MSMEs in their Net Zero and carbon credit journey:
- The NAPCC scheme (National Action Plan on Climate Change) supports green projects with financial aid.
- PAT (Perform, Achieve, and Trade) scheme allows MSMEs to earn tradable credits by improving energy efficiency.
- Under the credit guarantee scheme for green projects, financial support for MSMEs in adopting sustainable practices.
- GCF (Green Climate Fund) offers grants and low-interest loans for eco-friendly projects.
Conclusion: MSMEs as catalysts for Net Zero

MSMEs play a vital role in the global Net Zero mission. By adopting sustainable practices and earning carbon credits, they not only reduce their environmental footprint but also unlock new revenue streams and improve their competitiveness.
As the carbon market grows, MSMEs have a significant opportunity to monetise their green initiatives, strengthen their brand value, and contribute to a sustainable and resilient future.
Darshana Thakkar is an MSME Transformation specialist and Founder of Transformation – The Strategy HUB. With an Electrical engineering and MBA in business operations background, she has 28 years of hardcore industrial experience in transforming Small businesses. She helps MSMEs define growth paths, derive marketing strategies, improve business operations, adopt digital Transformation, and increase profitability.Darshana Thakkar is an author, speaker, and TV panelist. Her achievements, journey, and interviews have been featured in several newspapers, Premium business magazines, and TV.
She has won several regional, national, and international awards and is famous as an MSME activist and women's business leader. Her consulting venture, Transformation, was listed among the most trusted consulting companies in 2022 and among the top 50 consulting companies for MSME in 2023. She holds a few honorary positions in industry associations.
Major achievements:
- Winner of Global Women Leader -2023 by Global Women Leadership Award
- MSME Honor award-2022 -Champion of Cause by Tally Solutions
- Winner of Gujarat Women's Leader Award – 2021
She is associated with a few other premier institutes as
- Certified Women Director & Independent Director by IICA, MCA, GoI.
- Member of the Board of Management at Makarpura GIDC Industrial Estate Cooperative Bank Ltd.
- National President: WICCI-Entrepreneurship Development Council
- Trainer, Startup mentor, & Jury member at CED, Government of Gujarat.